After years of service, you’ve faced tough missions, made critical decisions, and led with discipline. Now that you're home, you might be wondering: What’s next for me?
Whether you're exploring a brand-new career, looking to move up in your current field, or simply searching for your next mission, one thing is clear—today’s opportunities often require updated skills, specialized knowledge, and strong industry connections.
But you may be thinking:
- Can I afford to go back to school?
- Do I even have the time, with work, family, and life all in motion?
🎉 Here's the good news: Thanks to the GI Bill, you can cover your tuition, housing, and even living costs. And with flexible hybrid programs, you don’t have to choose between your education and your responsibilities—you can do both.
Who Can Use GI Bill Benefits?
If you’ve served after 9/11, there’s a good chance you qualify for GI Bill benefits.
You May Be Eligible If:
- You served at least 90 days of active duty (with or without breaks) on or after September 11, 2001.
-
You received a Purple Heart after 9/11 and were honorably discharged—no matter how long you served.
-
You served 30 continuous days on or after 9/11 and were honorably discharged due to a service-connected disability.
-
You’re the spouse or dependent child (age 18–26) using benefits that a qualifying Veteran or service member transferred to you.


What Doesn’t Count?
There are a few situations where your service may not count toward GI Bill eligibility, like:
-
Being assigned by your branch to a civilian school for courses similar to civilian classes.
-
Serving as a cadet or midshipman at a service academy.
-
Doing initial skills or training only in the Guard or Reserves under Title 10, Section 12103(d).
-
Being called to duty under certain sections of Title 10 or Title 14 that don’t qualify.
-
Serving in the National Guard full-time for reasons outside of organizing, recruiting, or training under Title 32, Section 502(f).
⚠️ Heads up: If your only period of service started on or after August 1, 2011, and you qualify for more than one VA education benefit, you’ll need to choose just one to use.
What the GI Bill Actually Covers
With GI Bill benefits, you could generally get up to 36 months of education benefits that cover not just tuition but also housing, training costs, and more.
* If you have 2 or more qualifying periods of active duty, you may qualify for up to 48 months of benefits.
Overview:
Tuition
If you’re eligible for the full benefit, the Department of Veterans Affairs will pay 100% of in-state, public school tuition and fees—directly to your school. That means you won’t have to front the bill, and you can focus on your education.
You qualify for 100% of the full benefit if:
-
You served at least 36 months (1,095 days) on active duty, or
-
You received a Purple Heart on or after September 11, 2001, and were honorably discharged, or
-
You served 30 continuous days on or after 9/11 and were discharged for a service-connected disability
Served less than 36 months? You still qualify for a percentage of the benefit based on your service time:
(910–1,094 days)
(730–909 days)
(730–909 days)
(180–544 days)
Here’s how it breaks down by school type:
Monthly Housing Allowance (MHA)
Your Monthly Housing Allowance (MHA) is one of the most valuable GI Bill benefits, helping cover the cost of living while you're in school.
How Your MHA is Calculated
Formula: Final MHA = BAH (ZIP code) × Eligibility Tier % × Rate of Pursuit %
$3,987 (San Diego) × 100% (active duty for at least 1,095 days)× 60%(7/12 credits, rounded to the nearest tenth)=$2,392
Your class location: MHA is based on your school's zip code, not your home address.
- Use the Department of Defense’s BAH (Basic Allowance for Housing) rate for an E-5 with dependents.
Your eligibility tier: Based on how long you served on active duty. See: Post-911 Eligibility.
Your rate of pursuit: Depends on how many credits or clock hours you’re enrolled in.
- To be eligible for MHA, your rate of pursuit must be more than 50%. That means you need to be enrolled in more than half of what your school considers full-time.
- For example, if full-time at your school is 12 credits, you must take at least 7 credits to receive MHA. Taking only 6 credits or fewer would make you ineligible for the housing stipend.
To estimate your 2025 BAH, follow these steps:
-
Visit the BAH Calculator: Use the 2025 BAH Calculator.
-
Enter Your Details:
-
ZIP Code: Input your zip code (example: 92101 for San Diego)
-
Year: Select 2025.
-
Pay Grade: Choose E-5
-
-
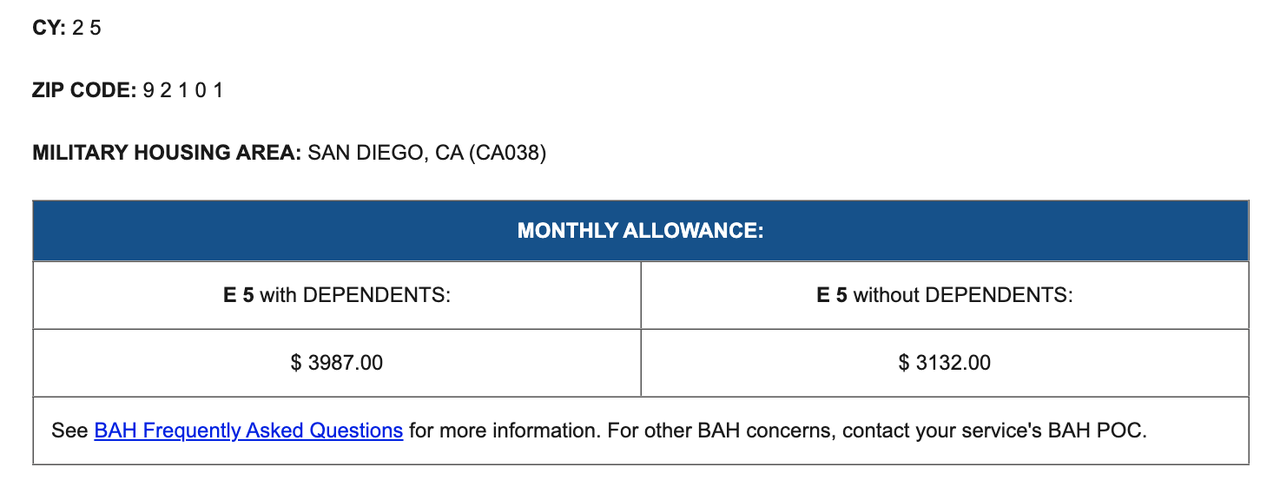
View Your BAH Rate:
-
For example, in 2025, an E-5 with dependents in San Diego receives approximately $3,987 per month.
-
MHA for Fully Online Programs
Formula: Final MHA = $1,169 (Year 2025) × Eligibility Tier % × Rate of Pursuit %
$1,169 × 100% (active duty for at least 1,095 days)× 60%(7/12 credits, rounded to the nearest tenth)=$701
If you’re taking 100% online courses or you’re at a foreign school, your MHA will be based on half the national average housing rate (Year 2025: $1,169), not your school's zip code.
When You’re Not Eligible for MHA
You’re not eligible for an MHA payment if any of these are true:
Book Stipends
The government will pay you up to $1,000 each academic year for books and supplies.
College or University
-
Up to $41.67 per credit hour
-
Up to 24 credits per year
(Prorated by the percentage of benefits you’re eligible for)
Non-College-Degree School
-
Up to $83 per month
The government will pay this money to you at the beginning of each term or enrollment period.
Money to help you move from a rural area to go to school
If you are relocating from a highly rural area so you can attend school, you may be eligible for a one-time $500 payment to help cover your moving expenses.
This Must be True
You live in a county with 6 or fewer people per square mile, according to the most recent U.S. Census.
One of These Must be True
You need to relocate at least 500 miles to attend school.
You must travel by air to attend school because no ground transportation is reasonably available.
Why Hybrid Programs Make It Possible
As mentioned earlier, the MHA you get depends on whether you're enrolled in fully online courses.
As you can see through the comparison, taking classes in person can qualify you for a higher MHA compared to fully online learning.
The good news is that to get a higher MHA, you don't need to be fully on-site. You can choose to enroll in hybrid programs, which allow you to balance your study, work, and life.
Benefits of Hybrid Programs
Higher MHA:
As long as you attend at least one in-person class, you're eligible for the full MHA—much more than the reduced rate for 100% online learning.



Flexible Scheduling:
Most hybrid programs combine online lectures with occasional in-person sessions, making it easier to keep working, care for your family, or manage other responsibilities.
No Need to Relocate Full-Time:
You can attend a school in a high MHA zip code without needing to live near campus full-time, helping you save on rent and commute.
More Interaction and Support:
Hybrid formats still give you access to on-campus resources, peer networks, and faculty, without the full-time classroom commitment of a traditional program.
VA-Approved and MHA-Eligible:
Many hybrid programs are fully VA-approved, so you can use your GI Bill benefits and still receive financial support for both tuition and housing.
Overall, hybrid programs are an ideal option for veterans who want career development, educational growth, and financial support, without sacrificing their current lifestyle.

Overall, hybrid programs are an ideal option for veterans who want career development, educational growth, and financial support, without sacrificing their current lifestyle.

How to Maximize Your Benefits?
-
Attend at least one on-campus class per term.
-
Take more than 50% of a full-time course load (e.g., 7+ credits if full-time is 12).
-
Choose a school in a high-BAH area to receive a higher housing payment.
-
Confirm VA approval for your program and format with your school’s certifying official.
Hybrid programs offer flexibility and access to full MHA benefits—helping you balance school, work, and life while making the most of your GI Bill.
VA–Approved Hybrid Programs in California
Westcliff University
CIAM (California Institute of Advanced Management)
Sofia University
-Jul-26-2025-01-32-49-6717-AM.jpg?width=1190&height=1190&name=Untitled%20design%20(1)-Jul-26-2025-01-32-49-6717-AM.jpg)
How to Apply for GI Bill Benefits
Step 1: Apply to Your School or Program
-
Choose a VA-approved institution (you can check via the WEAMS Institution Search Tool).
-
Complete the school’s admissions process and get accepted.
-
Enroll in a degree, certificate, or training program.


Step 2: Apply for VA Benefits
-
Submit VA Form 22-1990 (Application for Education Benefits) via VA.gov.
-
Wait for the Certificate of Eligibility (COE) from the VA.
Step 3: Coordinate with Your School’s VA Certifying Official
-
Take your COE and school acceptance letter to your school's VA Certifying Official.
-
They will complete and submit VA Form 22-1999 (Enrollment Certification) to the VA.

Step 5: Verify Enrollment Monthly
-
Use WAVE (Web Automated Verification of Enrollment) or phone (Calling 877-823-2378) to verify your enrollment each month.

-Jul-26-2025-01-32-49-6717-AM.jpg?width=1190&height=1190&name=Untitled%20design%20(1)-Jul-26-2025-01-32-49-6717-AM.jpg)
Other Educational Benefits for Veterans
List of Veteran Benefits
- Housing stipend (MHA)
- Book stipend (up to $1,000 per year)
- Relocation fee (up to $500)
- Federal student loans
- Work-Study opportunities
Why the GI Bill Stands Out
Comprehensive Coverage
The Post-9/11 GI Bill covers tuition, housing (MHA), books, and fees—often with no out-of-pocket costs at public schools.
Monthly Housing Allowance (MHA)
This benefit alone can be worth thousands per month, especially if you attend in person or in a hybrid format.
Flexibility Across Programs
You can use the GI Bill for undergraduate, graduate, vocational training, online or hybrid programs, and even some certifications.
Transferable to Family
If you’re not using it, you may be able to transfer it to a spouse or child—something most education benefits don’t offer.
Supplemented by Other Benefits
You can combine it with the Yellow Ribbon Program to cover private or out-of-state tuition, and pair it with FAFSA or scholarships if needed.
-2.jpg?width=1190&height=1190&name=Untitled%20design%20(4)-2.jpg)
.jpg?width=1200&height=675&name=Untitled%20design%20(2).jpg)
When Other Options Might Be Better
The GI Bill offers the broadest coverage, most financial support, and greatest flexibility—making it the go-to choice for most veterans planning to pursue higher education or career training.


